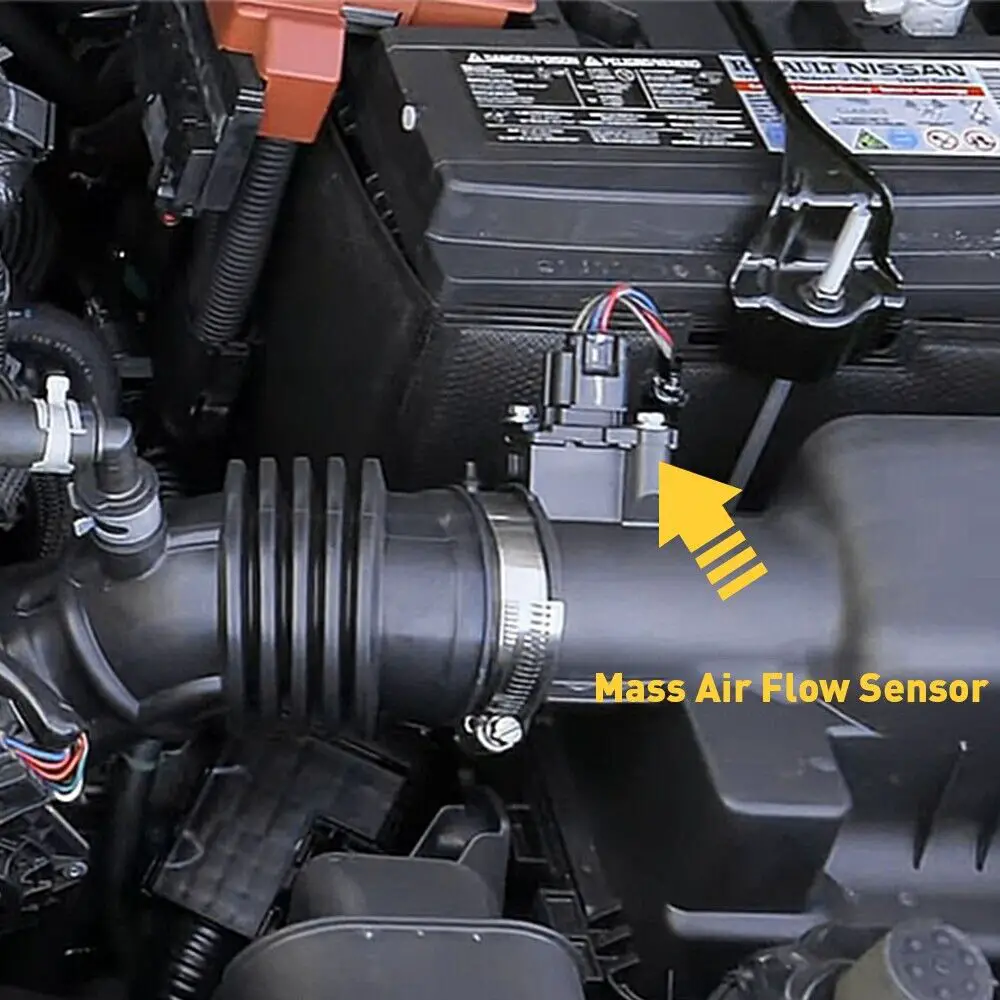
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is a critical component in today’s automobiles. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring the engine operates efficiently and maintains optimal performance. Understanding MAF sensors and their functions is essential for anyone who owns or works on a vehicle. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of MAF sensors, covering topics like diagnosing issues, replacement, cleaning, and more.
As we progress through this article, we will answer key questions, providing you with the knowledge and insights you need to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s MAF sensor. Whether you’re a seasoned car enthusiast or a novice driver, this information will empower you to address MAF sensor-related concerns and maintain your vehicle’s health.
Our structured approach will cover various aspects, from the basics of what an MAF sensor does and how it operates, to the telltale signs of a failing sensor and the possible consequences of neglecting its maintenance. We will also explore the costs associated with MAF sensor replacement and provide step-by-step instructions on how to replace or clean it.
Additionally, we will compare MAF sensors to their counterpart, the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor, and discuss the implications of MAF sensor problems on transmission. Furthermore, we will address the question of whether you can drive without a MAF sensor and the potential consequences of doing so.
By the time you finish reading this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of MAF sensors and how they impact your vehicle’s performance. Whether you’re troubleshooting issues or seeking to optimize your car’s operation, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions.
Also Read: Adaptive Cruise Control Problems – A Comprehensive Guide
What does the Mass Air Flow sensor do?

The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is a crucial component of a vehicle’s engine management system, responsible for measuring the amount of air entering the engine. This information is essential for the engine control unit (ECU) to determine the precise amount of fuel needed to maintain the air-to-fuel ratio required for efficient combustion. In essence, the MAF sensor plays a pivotal role in ensuring the engine runs optimally.
When you step on the accelerator pedal, the throttle opens, allowing air to flow into the engine. The MAF sensor is strategically positioned in the air intake system to monitor this incoming air. It uses various methods, depending on its design, to detect the volume and sometimes the temperature of the incoming air. This data is then relayed to the ECU, which, in turn, adjusts the fuel injection and ignition timing to achieve the right air-to-fuel mixture for combustion.
How does a Mass Air Flow sensor work?
MAF sensors work based on a variety of principles, but the most common type is the hot wire MAF sensor. This type of sensor has a thin wire or film heated by an electrical current. As incoming air flows over the hot wire, it cools the wire down. The amount of cooling is directly proportional to the volume of air passing through the sensor. By measuring the change in temperature of the wire, the sensor can accurately determine the mass of air entering the engine.
In some MAF sensors, instead of a hot wire, a hot film or hot plate is used. These work on similar principles, with the temperature change providing a measurement of the air mass.
The sensor outputs an electrical signal to the ECU, which corresponds to the mass of air flowing through it. The ECU interprets this signal and makes real-time adjustments to the fuel injector pulse width and ignition timing to maintain the optimal air-fuel mixture, ensuring efficient combustion and engine performance.
Mass Air Flow Sensor Diagram:
To provide a clearer understanding of the MAF sensor’s components and their functions, here’s a simple diagram:

- Air Intake
This is where the ambient air is drawn into the MAF sensor for measurement.
- Hot Wire or Film
The core sensing element, which heats up and measures temperature changes as air flows over it.
- Electrical Connection
The wires that transmit the sensor’s output signal to the ECU.
- Housing
The protective casing that encloses the sensor, shields it from external elements.
- Sensor Wiring
Connects the sensor to the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Electrical Connector
Links the sensor to the vehicle’s wiring harness.
What are the symptoms of a bad Mass Air Flow sensor?

A malfunctioning Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor can manifest a range of symptoms, which, if left unaddressed, can lead to decreased engine performance and efficiency. Some common signs of a bad MAF sensor include:
- Poor Performance
An inaccurate MAF sensor can cause the engine to receive incorrect data regarding the air intake. As a result, the engine may struggle to produce the necessary power, leading to reduced acceleration and overall performance.
- Rough Idling
A bad MAF sensor may cause erratic idling, where the engine speed fluctuates or feels unstable when the vehicle is at a standstill. This can lead to discomfort and, in severe cases, stalling.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency
When the MAF sensor fails, it can cause the engine to run either too rich (excess fuel) or too lean (insufficient fuel). Either condition can lead to decreased fuel efficiency and increased emissions.
- Stalling or Hesitation
The engine might stall or hesitate during acceleration due to improper air-fuel mixture, making the vehicle less responsive and potentially unsafe.
- Check Engine Light
A failing MAF sensor often triggers the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system, causing the “Check Engine” or “Service Engine Soon” light to illuminate on the dashboard. This is an indicator to have the sensor inspected.
Can a Mass Air Flow sensor cause a misfire?
Yes, a faulty MAF sensor can cause engine misfires. Misfires occur when the air-fuel mixture is not balanced correctly, leading to incomplete combustion in one or more cylinders. Since the MAF sensor is responsible for measuring incoming air and helping the engine control unit (ECU) adjust the fuel injection, a malfunctioning MAF sensor can provide inaccurate air intake data. This, in turn, can result in an incorrect air-fuel mixture, causing misfires.
Engine misfires can lead to a range of issues, including reduced power, poor fuel efficiency, increased emissions, and potential damage to the catalytic converter. Therefore, addressing MAF sensor problems is essential to prevent or resolve misfire issues.
Why would a car run better with the Mass Air Flow sensor unplugged?

In some cases, a vehicle may seem to run better with the MAF sensor unplugged, although this is not a recommended long-term solution. The MAF sensor provides crucial data to the ECU to maintain the proper air-fuel mixture, and unplugging it disrupts this feedback loop.
Here are some scenarios where a car might run better with the MAF sensor unplugged:
- Sensor Contamination
If the MAF sensor is contaminated with dirt, oil, or other substances, it may provide inaccurate readings. Unplugging it can temporarily bypass these inaccuracies and allow the engine to run more smoothly.
- Failed MAF Sensor
In cases where the MAF sensor has completely failed, it can send erratic or incorrect signals to the ECU. Disconnecting the sensor prevents the ECU from relying on this flawed data, which might result in improved performance.
- Limited Operation
Some vehicles may have a failsafe mode that adjusts the engine’s parameters when the MAF sensor is disconnected. This mode can help the vehicle run, albeit with reduced performance, to get to a repair facility in the event of sensor failure.
It’s important to note that running a vehicle with the MAF sensor unplugged is not a long-term solution. It can negatively affect performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. The MAF sensor should be properly diagnosed and, if necessary, replaced or cleaned to ensure the engine operates optimally.
What causes Mass Air Flow sensors to fail?

Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor failures can occur due to various factors, and understanding these potential causes is essential for effective diagnosis and maintenance. Here are some common reasons why MAF sensors may fail:
- Contamination
One of the leading causes of MAF sensor failure is contamination. Dust, debris, oil, or other particles from the air intake can accumulate on the sensor’s hot wire or film, affecting its accuracy. This contamination disrupts the MAF sensor’s ability to measure incoming air correctly.
- Wear and Tear
Over time, MAF sensors can experience wear and tear, especially in harsh environments or with high mileage. This can result in sensor degradation, making it less precise in its air intake measurements.
- Electrical Problems
Issues with the sensor’s electrical components or wiring can lead to failure. Broken wires, loose connections, or problems with the sensor’s heating element can all affect its performance.
- Age and Mileage
Like many components in a vehicle, MAF sensors can simply wear out with age and extensive use. This often leads to a decline in accuracy and performance.
- Oil Vapor Buildup
In some cases, oil vapor from the engine can make its way into the air intake system. This can coat the MAF sensor, causing contamination and failure.
- Exposure to Extreme Temperatures
Extreme heat or cold can affect the MAF sensor’s performance. Rapid temperature changes can lead to the sensor malfunctioning or providing inaccurate readings.
How to test a Mass Air Flow sensor

Testing a MAF sensor is essential to confirm if it’s the root cause of any performance issues in your vehicle. Here’s a step-by-step guide to diagnosing MAF sensor issues:
- Prepare the Tools: You’ll need a digital multimeter, a set of safety goggles, and the vehicle’s service manual for reference.
- Locate the MAF Sensor: Find the MAF sensor in your vehicle’s air intake system. It’s typically located between the air filter box and the throttle body. The sensor may be connected to an electrical plug.
- Safety First: Put on your safety goggles to protect your eyes from any debris or contaminants that may be present.
- Disconnect the Electrical Plug: Carefully unplug the electrical connector from the MAF sensor.
- Measure the Sensor’s Resistance: Set your multimeter to measure resistance (ohms) and carefully place the meter leads on the sensor’s electrical terminals. Consult your vehicle’s service manual for the specific resistance values that should be within the acceptable range.
- Inspect for Contamination: Visually inspect the sensor for any contamination, such as dirt, oil, or debris. If you notice contamination, the sensor may need cleaning or replacement.
- Reconnect the Sensor: Reconnect the electrical plug to the sensor.
- Read Error Codes: If you have access to an OBD-II scanner (my recommended selection), you can use it to retrieve error codes related to the MAF sensor. These codes can provide additional information about sensor performance.
- Test Drive: After checking the sensor and resolving any contamination issues, take the vehicle for a test drive. Pay attention to the symptoms that led you to suspect MAF sensor problems. If the issues persist, further diagnosis may be required.
Also Read: Cabin Air Filter vs Engine Air Filter: Understanding the Key Differences
Mass Air Flow Sensor Codes
When an MAF sensor malfunctions, it often triggers error codes in the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system. These codes provide valuable information about the specific issue. Common error codes related to MAF sensor problems include:
- P0100: MAF Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- P0101: MAF Sensor Range/Performance Problem
- P0102: MAF Sensor Circuit Low Input
- P0103: MAF Sensor Circuit High Input
- P0104: MAF Sensor Circuit Intermittent
Understanding these error codes can help in diagnosing the nature of the problem and whether it’s related to the sensor itself, its circuitry, or another issue in the system. If you retrieve any of these error codes, it’s an indication that you should inspect, clean, test, or potentially replace the MAF sensor as necessary.
Can I clean a Mass Air Flow sensor?
Yes, you can clean a Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor, and in fact, regular maintenance can help extend its lifespan and maintain your vehicle’s performance. Cleaning the MAF sensor is a straightforward process that can be done by following these steps:
- Safety Precautions: Before you begin, ensure the vehicle is turned off and the engine is cool. Use safety goggles and work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling any fumes.
- Locate the MAF Sensor: The MAF sensor is typically positioned in the air intake system between the air filter box and the throttle body. Refer to your vehicle’s service manual to pinpoint its exact location.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully unplug the electrical connector from the MAF sensor to prevent any electrical damage during the cleaning process.
- Remove the MAF Sensor: Depending on your vehicle, the MAF sensor may be housed in a separate assembly. Remove any screws or clamps holding it in place.
- Inspect for Contamination: Examine the sensor for any visible contamination. Look for dirt, oil residue, or other debris on the sensor’s hot wire or film.
- Clean the MAF Sensor: To clean the MAF sensor, use an MAF sensor cleaner spray, which is specifically designed for this purpose. Do not use other cleaning agents, as they may damage the sensor. Carefully and thoroughly spray the cleaner directly onto the sensor’s wire or film. Allow it to dry completely.
- Reassemble and Reconnect: Once the sensor is dry, carefully reassemble and reconnect it, making sure all components are securely in place.
- Clear Error Codes: If your vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system triggered error codes due to MAF sensor issues, you may need to clear these codes using an OBD-II scanner.
Cleaning the MAF sensor can improve its performance by removing contaminants that may have built up over time. It’s a good practice to clean the MAF sensor at regular intervals, especially if you drive in dusty or dirty environments.
How long does a Mass Air Flow sensor last?
The lifespan of a MAF sensor can vary depending on factors such as the quality of the sensor, driving conditions, and vehicle maintenance. On average, a well-maintained MAF sensor can last between 100,000 to 150,000 miles (160,000 to 240,000 kilometers). However, it’s not uncommon for some sensors to last longer, while others may fail prematurely.
Signs that your MAF sensor may need replacement include:
- Worsening Performance
If your vehicle experiences reduced power, poor acceleration, or decreased fuel efficiency, it may be a sign that the MAF sensor is failing.
- Check Engine Light
If the “Check Engine” or “Service Engine Soon” light is illuminated on your dashboard and diagnostic codes relate to the MAF sensor, this is an indication that the sensor may be failing.
- Rough Idling or Stalling
Inconsistent idling, engine hesitation, or stalling are common symptoms of a failing MAF sensor.
- Excessive Emissions
A malfunctioning MAF sensor can lead to increased emissions, which may result in a failed emissions test.
Mass Air Flow Sensor Replacement Cost
The cost of replacing a Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor can vary depending on several factors, including the make and model of your vehicle, labor rates in your area, and whether you choose an original equipment manufacturer (OEM) or aftermarket MAF sensor. On average, the cost of MAF sensor replacement typically ranges from $100 to $300 for parts and labor combined.
- Parts Cost
The price of a new MAF sensor can range from $50 to $150 or more, depending on the brand and quality. OEM sensors are generally more expensive than aftermarket options, but they are designed to meet the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Labor Cost
Labor costs for MAF sensor replacement can vary widely based on your location and the repair shop’s rates. On average, labor costs can range from $50 to $150 or more.
It’s important to note that if you have some mechanical skills and the necessary tools, you can save on labor costs by replacing the MAF sensor yourself. However, if you’re uncertain about the procedure, it’s advisable to have a professional mechanic handle the replacement to avoid any potential mistakes.
How to replace a Mass Air Flow sensor
If you’re a DIY enthusiast and feel comfortable working on your vehicle, you can replace the MAF sensor yourself by following these steps:
- Gather Tools and Parts
You’ll need the new MAF sensor, a set of wrenches or sockets, safety goggles, and a digital multimeter for testing.
- Safety First
Ensure the vehicle is turned off, the engine is cool, and wear safety goggles to protect your eyes.
- Locate the MAF Sensor
Refer to your vehicle’s service manual to locate the MAF sensor. Typically, it’s positioned in the air intake system between the air filter box and the throttle body.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector
Carefully unplug the electrical connector from the MAF sensor.
- Remove the Old MAF Sensor
Depending on your vehicle, you may need to remove screws or clamps holding the sensor in place. Once removed, take note of the sensor’s orientation to install the new one correctly.
- Test the New Sensor
Before installation, it’s a good practice to test the new MAF sensor’s resistance with a multimeter. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure it’s functioning properly.
- Install the New MAF Sensor
Carefully place the new MAF sensor in the same orientation as the old one and secure it with the screws or clamps.
- Reconnect the Electrical Plug
Plug the electrical connector into the new MAF sensor.
- Clear Error Codes
If your vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system triggered error codes due to MAF sensor issues, use an OBD-II scanner to clear these codes.
- Test Drive
After the replacement, take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure that the symptoms that led you to replace the MAF sensor have been resolved.
What to do after replacing a Mass Air Flow sensor
After replacing the MAF sensor, there are some important considerations to ensure optimal performance:
- Reset the ECU
To allow the engine control unit (ECU) to adapt to the new sensor, it’s a good practice to reset the ECU. You can do this by disconnecting the vehicle’s battery for a few minutes and then reconnecting it.
- Monitor Performance
After replacement, closely monitor the vehicle’s performance for any signs of improvement. Pay attention to acceleration, fuel efficiency, and overall engine operation.
- Address Any Remaining Issues
If you continue to experience performance problems, it’s possible that the MAF sensor replacement did not resolve the underlying issue. In such cases, consult a professional mechanic for further diagnosis.
- Regular Maintenance
To maintain the MAF sensor’s accuracy, consider cleaning it at regular intervals as part of your vehicle’s routine maintenance.
Mass Air Flow vs. Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
In the complex world of engine management and performance optimization, Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensors and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensors play distinct but interconnected roles. Understanding their differences and when to use each sensor is crucial for efficient engine operation.
Differences and Functions
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
- Function
MAF sensors measure the mass of incoming air by analyzing the flow rate. They calculate the exact amount of air entering the engine, helping the engine control unit (ECU) adjust the fuel injection to maintain the ideal air-fuel ratio.
- Placement
MAF sensors are typically positioned in the air intake system, between the air filter box and the throttle body.
- Measurement Method
MAF sensors use various technologies, such as hot wires, hot films, or hot plates, to measure the airflow.
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
- Function
MAP sensors measure the pressure within the intake manifold. This pressure data helps the ECU determine the engine’s load, as it’s indicative of how much air the engine is drawing in.
- Placement
MAP sensors are directly connected to the intake manifold, where they can monitor the vacuum or pressure conditions.
- Measurement Method
MAP sensors use a diaphragm or semiconductor to measure the pressure differential between the intake manifold and the atmosphere.
When to Use an MAF Sensor and When to Use a MAP Sensor
MAF Sensor Usage
- Precision
MAF sensors are highly precise in measuring the actual amount of air entering the engine, which is essential for maintaining an accurate air-fuel mixture. They are commonly used in modern fuel-injected vehicles for optimal fuel management.
- Variable Engine Load
MAF sensors are particularly useful in scenarios where engine load can vary widely, such as during acceleration, deceleration, or idle. They provide real-time data that allows the ECU to adjust the fuel delivery accordingly.
MAP Sensor Usage
- Engine Load Indication
MAP sensors excel at indicating the engine’s load. They are valuable in naturally aspirated engines or in situations where the engine load is relatively constant. This makes them common in older vehicles or in applications where simple engine management is sufficient.
- Turbocharged and Supercharged Engines
In forced induction systems like turbochargers and superchargers, MAP sensors are often preferred as they can effectively measure changes in manifold pressure caused by forced induction.
The choice between a MAF sensor and a MAP sensor is typically determined by the vehicle’s design and the requirements of the engine management system. Many modern vehicles use a combination of both sensors to ensure precise control over the air-fuel mixture under various driving conditions.
Can a bad Mass Air Flow sensor cause transmission problems?
Yes, a malfunctioning Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor can potentially cause transmission problems, though the direct relationship is not as common as its impact on engine performance. Here’s how MAF sensor issues can indirectly affect the transmission:
- Incorrect Air-Fuel Mixture
When a MAF sensor fails or provides inaccurate readings, it can disrupt the engine’s ability to maintain the correct air-fuel mixture. If the engine runs too rich (excess fuel) or too lean (insufficient fuel), it can lead to reduced power and poor performance. This reduced power may cause the transmission to shift differently, affecting the vehicle’s overall drivability.
- Reduced Engine Performance
A malfunctioning MAF sensor can lead to engine misfires, poor acceleration, and rough idling. These issues can indirectly stress the transmission, as it may need to compensate for the lack of power by adjusting shift points and torque converter lock-up. The constant need for these adjustments can lead to increased wear and tear on the transmission components.
- Potential Stalling or Hesitation
In extreme cases, a severely malfunctioning MAF sensor can lead to engine stalling or hesitation. This can create abrupt changes in engine load, causing the transmission to respond with harsh or erratic shifting patterns.
- Increased Emissions
A problematic MAF sensor can result in higher emissions, which may not only affect the environment but also lead to regulatory issues. If the vehicle fails emissions tests, it can result in further complications, including potential restrictions on its operation.
It’s important to address MAF sensor issues promptly to prevent these indirect transmission problems. Once the MAF sensor is functioning correctly, the engine can operate more efficiently, which, in turn, reduces the potential stress on the transmission. Moreover, resolving MAF sensor problems can lead to improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and a smoother overall driving experience.
How to Reset a Mass Air Flow Sensor
Resetting a Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is typically not a specific procedure like resetting a computer. Instead, it involves clearing the error codes and allowing the engine control unit (ECU) to relearn the MAF sensor’s parameters after replacement or cleaning. Here’s how you can reset a MAF sensor:
- Disconnect the Battery
To reset the ECU and clear any stored error codes, disconnect the vehicle’s battery. Start with the negative terminal (black cable) and then the positive terminal (red cable). Ensure the vehicle is turned off before disconnecting the battery.
- Wait for a Few Minutes
Leave the battery disconnected for about 15-30 minutes. This allows the ECU’s capacitors to discharge, which effectively clears any stored data.
- Reconnect the Battery
After the waiting period, reconnect the battery in reverse order, starting with the positive terminal and then the negative terminal. Ensure the connections are secure.
- Turn the Ignition On
Turn the ignition to the “On” position without starting the engine. This will power up the vehicle’s systems.
- Start the Engine
Start the engine and allow it to idle. The ECU will now begin relearning and adapting to the newly replaced or cleaned MAF sensor. It may take some time for the ECU to fully adapt, so be patient.
- Test Drive
After the engine has idled for a few minutes, take the vehicle for a test drive. Pay attention to the performance and ensure that any issues that led to MAF sensor replacement or cleaning have been resolved.
Conclusion
Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensors are integral to modern vehicle performance. They accurately measure incoming air, enabling precise control of the air-fuel mixture, which is crucial for efficient combustion. In this comprehensive guide, we’ve covered the functions of MAF sensors, how they work, signs of failure, diagnosis, cleaning, replacement, and the associated costs. We’ve also explored the impact of MAF sensor issues on engine and transmission performance, as well as when to use MAF versus Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensors.
Maintaining, diagnosing, and replacing MAF sensors when necessary is essential for optimal vehicle performance. Ignoring MAF sensor problems can lead to a range of issues, from poor power and fuel efficiency to engine misfires and transmission complications. By addressing these concerns promptly, you can ensure that your vehicle operates at its best, reducing emissions and improving the overall driving experience. Regular maintenance and attention to the health of your MAF sensor will keep your vehicle running smoothly for miles to come.