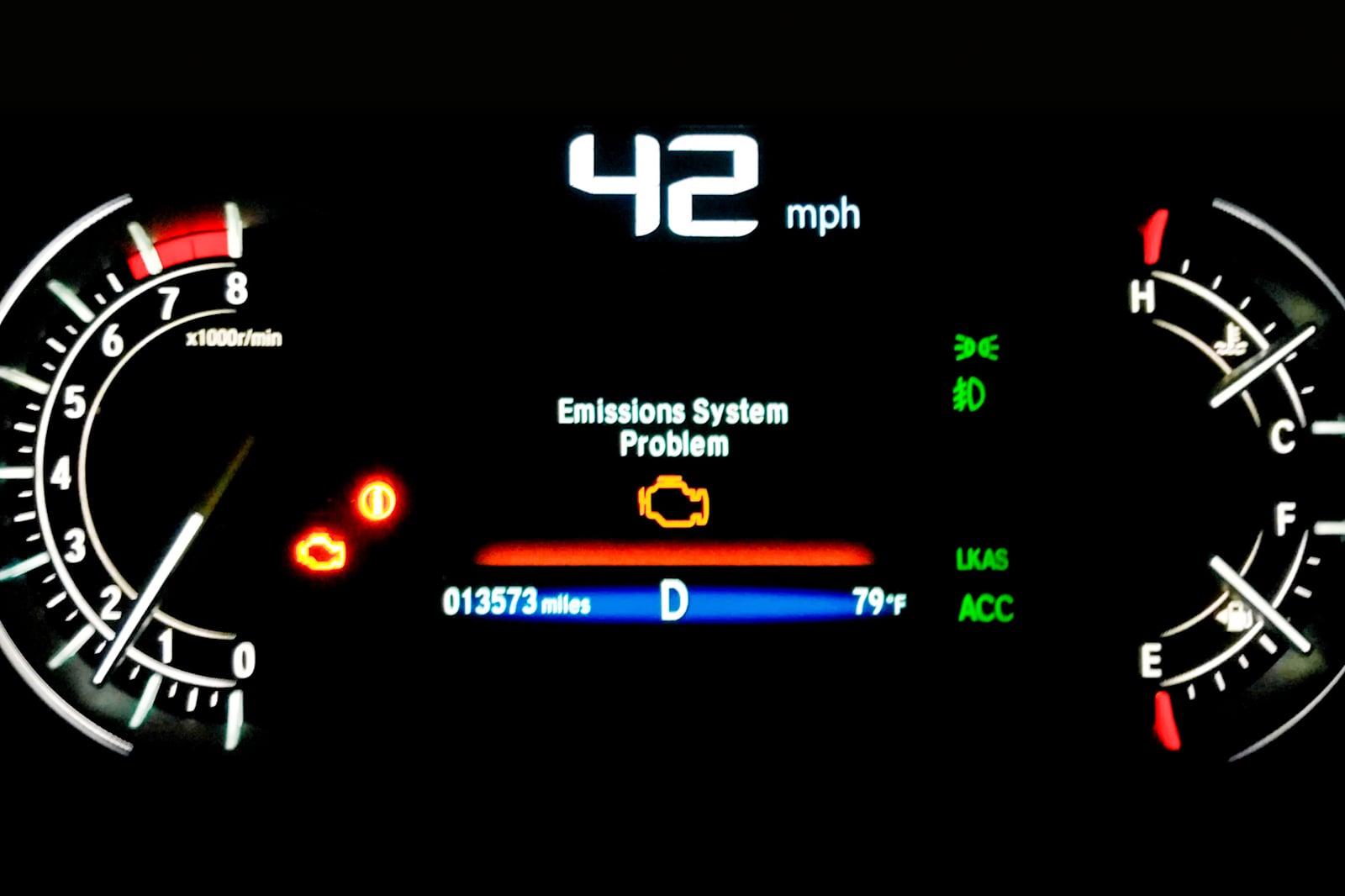
Navigating the complexities of vehicle maintenance can be daunting, especially when it comes to emissions.
The Honda Pilot, a trusted family SUV, is not immune to these challenges.
Owners may encounter Honda Pilot Emissions System Problems, which can range from minor sensor glitches to more significant exhaust issues.
Understanding the root causes is crucial for effective solutions.
This article delves into the intricacies of the Honda Pilot’s emissions system, shedding light on common problems and providing actionable advice to keep your vehicle running cleanly and efficiently.
Join us as we explore the path to a greener drive.
What Are The Common Signs Of Emissions System Failure In A Honda Pilot?
Recognizing the signs of emissions system failure in a Honda Pilot is key to maintaining its performance and environmental compliance. Here are the common indicators:
-
Check Engine Light
The most apparent sign is the illumination of the check engine light on the dashboard. This light can signal various issues, including those related to the emissions system.
-
Decreased Fuel Efficiency
If you notice a sudden drop in miles per gallon, it could be due to an emissions system problem affecting the engine’s air-to-fuel ratio.
-
Rough Idling or Stalling
An emissions system issue can disrupt the engine’s operation, leading to rough idling, stalling, or difficulty starting the vehicle.
-
Unusual Noises
Hissing sounds from the exhaust system may indicate leaks or cracks that can affect emissions control.
-
Unpleasant Smells
A malfunctioning catalytic converter can produce a sulfur-like smell, akin to rotten eggs, indicating it’s not processing exhaust gases properly.
-
Failed Emissions Test
If your Honda Pilot fails an emissions test, it’s a clear sign that there’s a problem with the emissions system that needs to be addressed.
-
Performance Issues
You may experience a loss of power or acceleration, which can be caused by a clogged catalytic converter or issues with the oxygen sensors.
Related Post: What Is The Cost To Replace the Honda Pilot Timing Belt? – A Detail Explanation
How Can Faulty Sensors Impact The Emissions System Of A Honda Pilot?
Faulty sensors can significantly impact the emissions system of a Honda Pilot, leading to a range of issues that affect the vehicle’s performance and environmental footprint. Here’s how:
-
Oxygen Sensors
The oxygen sensors measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases, which is crucial for the engine’s computer to maintain the correct air-fuel mixture. If these sensors fail, the engine may run too rich or too lean, causing increased emissions and reduced fuel efficiency.
-
Cylinder Deactivation System
The Honda Pilot’s cylinder deactivation system is designed to improve fuel efficiency by shutting down some cylinders under certain conditions. Faulty sensors in this system can cause improper activation or deactivation of cylinders, leading to increased emissions and potential damage to the engine.
-
Fuel Injectors and High-Pressure Fuel Pumps
In newer models with direct fuel injection, sensors monitor the fuel injectors and high-pressure fuel pumps. Malfunctions in these sensors can lead to incorrect fuel delivery, resulting in higher emissions and possible engine misfires.
-
Catalytic Converter
Sensors also monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter. If these sensors send incorrect data, it may indicate a failing catalytic converter when it is actually functioning properly, or vice versa, leading to unnecessary replacements or ignored emissions issues.
-
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
The PCM relies on various sensors to regulate the emissions system. If the PCM receives incorrect information due to sensor failures, it may misinterpret this data, causing the malfunction indicator light to activate and potentially leading to incorrect diagnostic codes.
What Role Does The Catalytic Converter Play In Honda Pilot Emissions Issues?
The catalytic converter plays a pivotal role in the Honda Pilot’s emissions control system. It’s responsible for reducing the harmful pollutants emitted by the engine before they exit the vehicle’s exhaust system. Here’s how it functions and its significance:
-
Pollutant Conversion
The catalytic converter uses precious metals like platinum and palladium to catalyze a chemical reaction that transforms harmful carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances, such as nitrogen and water vapor.
-
Regulatory Compliance
By efficiently processing exhaust gases, the catalytic converter helps the Honda Pilot meet environmental regulations and standards for emissions.
-
Performance Impact
A well-functioning catalytic converter ensures optimal engine performance by minimizing the back pressure caused by the accumulation of exhaust gases.
-
Common Issues
Catalytic converters can face problems like clogging due to carbon buildup, which can lead to decreased engine performance and increased emissions. Additionally, a failed oxygen sensor can affect the air/fuel mixture, leading to poor catalytic converter efficiency.
-
Symptom Recognition
Recognizing symptoms of a failing catalytic converter, such as reduced fuel efficiency, rough idling, or a sulfur-like smell, is crucial for timely intervention and repair.

Is Your Honda Pilot’s Exhaust System Affecting Its Emission Performance?
The exhaust system of your Honda Pilot is a critical component in managing the vehicle’s emissions performance. This is how it can affect emission performance:
-
Exhaust Flow
The exhaust system is designed to channel exhaust gases away from the engine and through the exhaust pipe. Any obstruction or damage within the system can cause a restriction in flow, leading to increased back pressure. This can negatively impact engine efficiency and increase emissions.
-
Catalytic Converter
As part of the exhaust system, the catalytic converter’s role is to reduce harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful gases. If the converter is failing or clogged, it can’t perform this function effectively, leading to higher emissions levels.
-
Oxygen Sensors
These sensors are located in the exhaust system and measure the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases. The data they provide helps adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion. Faulty sensors can send incorrect information, causing the engine to run rich (too much fuel) or lean (not enough fuel), both of which can increase emissions.
-
Exhaust Leaks
Leaks in the exhaust system can allow exhaust gases to escape before they reach the catalytic converter, resulting in increased emissions. Common leak points include the exhaust manifold and the joints between exhaust system components.
The muffler’s primary function is to reduce noise, but it also affects the flow of exhaust gases. A damaged or rusted muffler can disrupt the flow and impact emissions.
-
EGR System
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system recirculates a portion of the exhaust gases back into the engine’s combustion chamber to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions. Issues with the EGR system can lead to higher emissions.
-
Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the exhaust system, including inspections for damage, leaks, and clogs, is essential to ensure it functions correctly and does not contribute to increased emissions.
Can Regular Maintenance Prevent Emissions System Problems In A Honda Pilot?
Regular maintenance is essential in preventing emissions system problems in a Honda Pilot. This is how it helps:
Engine Health: Regular oil changes and engine tune-ups ensure the engine runs smoothly. Clean oil reduces wear and tear on engine components, which can affect emissions.
Sensor Accuracy: Sensors play a crucial role in the emissions system. Regular checks can detect faults early, preventing incorrect data that could lead to increased emissions.
Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter reduces harmful emissions. Regular inspections can identify issues like clogging or damage before they become serious.
Fuel System: Maintaining the fuel system, including the fuel injectors and filters, ensures proper fuel delivery. This helps maintain the optimal air-fuel ratio, crucial for low emissions.
Exhaust System: Inspecting the exhaust system for leaks or damage ensures that exhaust gases are properly processed through the emissions control components.
EGR System: The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system reduces nitrogen oxide emissions. Regular checks can prevent blockages and ensure it operates correctly.
Diagnostic Checks: Using onboard diagnostics (OBD) to scan for error codes can identify potential emissions issues before they escalate.
Software Updates: Keeping the vehicle’s software up-to-date can prevent issues related to emissions, as manufacturers may release updates that improve system performance.
What Are The Environmental Impacts Of Emissions System Malfunctions?
Emissions system malfunctions can have significant environmental impacts, including:
Air Pollution: Malfunctions can lead to increased levels of pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and particulate matter (PM), contributing to smog and poor air quality.
Health Risks: These pollutants can pose serious health risks to humans, aggravating respiratory conditions such as asthma and leading to cardiovascular problems.
Climate Change: Excessive emissions of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO2) from malfunctioning systems contribute to global warming and climate change.
Ecosystem Damage: Air pollutants can lead to acid rain, which can damage forests, harm aquatic life in rivers and lakes, and degrade soil quality.
Visibility Reduction: Particulate matter from vehicle emissions can reduce visibility, leading to hazardous driving conditions and affecting the beauty of natural landscapes.
Regulatory Non-Compliance: Vehicles with malfunctioning emissions systems may fail to meet regulatory standards, leading to legal and financial consequences for owners.
How Do Honda Pilot Emissions Problems Affect Fuel Efficiency And Performance?
Emissions problems in a Honda Pilot can have a noticeable impact on both fuel efficiency and performance. Here’s how:
-
Fuel Efficiency
When the emissions system is compromised, the engine may not combust fuel as efficiently as it should. This can lead to a decrease in miles per gallon, as the engine compensates for the inefficiency by using more fuel.
-
Engine Performance
Issues such as clogged fuel injectors or a malfunctioning oxygen sensor can cause the engine to run poorly. This might manifest as reduced acceleration, power loss, or a rough idle, as the engine struggles to maintain optimal performance.
-
Air-Fuel Mixture
The emissions system helps regulate the air-to-fuel ratio necessary for the engine to run smoothly. If sensors are faulty or the system is otherwise impaired, the mixture can be off, leading to poor combustion and reduced engine power.
-
Exhaust Leaks
A leak in the exhaust system can cause an imbalance in the air/fuel ratio, which can trigger the check engine light and lead to increased emissions and decreased fuel efficiency.
-
Transmission Issues
Problems with the transmission can also affect emissions and performance. Rough shifting or delayed gear engagement can increase the engine’s workload, leading to higher emissions and reduced fuel economy.
What Steps Should You Take When You Encounter An Emissions System Alert?
When you encounter an emissions system alert in your Honda Pilot, it’s important to take systematic steps to address the issue. This is what you should do:
Don’t Panic: An emissions system alert doesn’t necessarily mean immediate danger, but it shouldn’t be ignored. It indicates that there’s a problem affecting the vehicle’s emissions control system.
Check the Dashboard: Look for the specific emissions-related warning light on your dashboard. It’s usually an engine-shaped icon or may explicitly say “check emissions system.”
Observe Performance: Pay attention to any changes in your vehicle’s performance, such as rough idling, stalling, or difficulty accelerating. These symptoms can help diagnose the issue.
Reduce Driving: If possible, limit your driving until the issue is resolved. Continuing to drive with an emissions problem can lead to more significant damage and higher repair costs.
Consult the Manual: Your Honda Pilot’s manual may provide information about the emissions system alert and suggest initial steps to take.
Perform a Visual Check: Safely inspect your vehicle for any obvious signs of damage or leaks in the emissions system components, such as the exhaust pipe or catalytic converter.
Use Onboard Diagnostics (OBD): If you have an OBD-II scanner, you can plug it into your vehicle to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These codes can give you a clearer idea of what’s causing the alert.
Seek Professional Help: Unless you have experience with car repairs, it’s advisable to take your vehicle to a certified mechanic or a Honda dealership. They can perform a more thorough diagnosis and repair any issues.
Address Recalls: Check if there are any recalls or technical service bulletins (TSBs) for your specific model related to emissions system problems.
Follow-up: After the repair, monitor your vehicle closely to ensure the problem doesn’t recur. Keep an eye on the dashboard for any new alerts.
Are There Recurring Emissions Issues Specific To Certain Honda Pilot Models?
Yes, certain Honda Pilot models have been known to experience recurring emissions issues. Here’s a summary of the problems specific to different generations:
First and Second Generation (2003-2015)
Early models primarily faced issues with catalytic converter or oxygen sensor failures. From 2006, front-wheel-drive first-generation models equipped with cylinder-deactivation hardware also encountered problems related to this feature.
Third Generation (2016-2019)
These models introduced direct fuel injection systems, which added complexity and new potential failure points. Issues in this generation may stem from the cylinder deactivation system or the direct fuel injection system, leading to emissions system alerts.
Common Problems Across Models
Defective oxygen sensors, failing catalytic converters, and faults in the cylinder deactivation system are recurring issues that can trigger emissions system warnings across various Honda Pilot models.
What Solutions Exist For Honda Pilot Owners Facing Emissions System Challenges?
Honda Pilot owners facing emissions system challenges have several solutions at their disposal to address and resolve these issues effectively:
-
Sensor and Actuator Inspection
Many emissions problems are related to faulty sensors or actuators. These components can often be replaced easily, restoring proper function to the emissions system.
-
Variable Cylinder Management (VCM) Issues
For models equipped with VCM, issues may arise from this system. It’s recommended to have a Honda specialist inspect the VCM unit, especially if it’s located in a difficult-to-access area like the rear cylinder head.
-
Wiring Harness Checks
Inspect the wiring harness for any faults. A wiring issue can lead to incorrect signals being sent to and from emissions components, causing malfunctions.
-
Fuel System Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the fuel system, including the fuel injectors and high-pressure fuel pumps, is crucial. Keeping these components clean and functioning properly can prevent many emissions-related problems.
-
Software Updates
Ensure that your vehicle’s software is up-to-date. Manufacturers may release updates that can improve the emissions system’s performance and resolve existing issues.
-
Use of Quality Fuel
Using high-quality fuel can help maintain the health of the emissions system and prevent issues related to fuel contaminants.
-
Avoid Excessive Idling
Excessive idling can lead to unnecessary strain on the emissions system. Minimizing idling time can help maintain system efficiency.
-
Professional Diagnostics
If the check emissions system message appears, use an OBD-II scanner to read the trouble codes. This will provide specific information about the issue, which can then be addressed by a professional mechanic.
-
Regular Vehicle Check-Ups
Schedule regular check-ups for your Honda Pilot to catch any potential emissions issues early and address them before they escalate.
Conclusion
Addressing Honda Pilot Emissions System Problems requires a blend of vigilance, knowledge, and timely action.
By understanding the common signs of emissions issues and embracing regular maintenance, owners can ensure their vehicle remains a reliable companion on the road.
It’s not just about keeping the check engine light off; it’s about contributing to a cleaner environment and enjoying the full performance of your Honda Pilot.
With the right approach, you can navigate the complexities of emissions systems, ensuring your Honda Pilot continues to drive smoothly and efficiently for years to come.