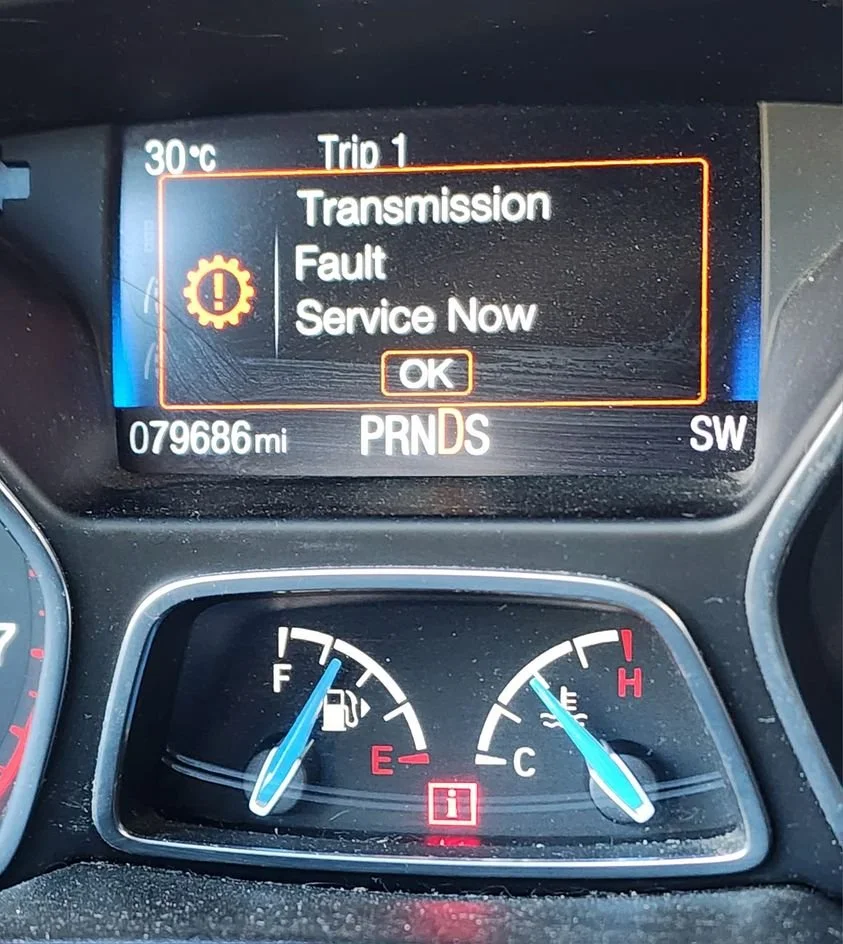
If you own a Ford vehicle with a 5.4 3-valve engine, you may have encountered some problems with it.
The Ford 5.4 3-valve engine is a V8 engine that belongs to the Modular family of Ford engines.
It was introduced in 2002 and featured some advanced technologies such as variable camshaft timing and three valves per cylinder.
However, these innovations also came with some drawbacks, such as spark plug failure, timing chain rattles, oil leaks, and more.
In this article, we will explore the common Ford 5.4 3-valve engine problems, their causes, symptoms, and solutions.
We will also discuss the reliability and performance of this engine and whether it is worth buying or not.
By the end of this article, you will have detailed coverage of the Ford 5.4 3-valve engine problems and how to deal with them.
What is a 5.4 3v Triton?
A 5.4 3v Triton is a type of engine that was used in some Ford vehicles, such as the F-150 and the Expedition. It is a 5.4-liter V8 engine with three valves per cylinder and variable camshaft timing. It was introduced in 2004 and replaced by the 5.0 Coyote engine in 2011.
What Are Ford 5.4 3 Valve Engine Problems?
1: Spark plug and coil failure
Spark plugs and coils are essential components of the ignition system, which creates the spark needed to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the engine cylinders. Spark plug and coil failure can occur due to various reasons, such as wear and tear, corrosion, oil or carbon deposits, overheating, or electrical issues. Some common symptoms of spark plug and coil failure are:
- Poor engine performance, such as loss of power, rough idle, misfires, or hesitation
- Reduced fuel economy and increased emissions
- Difficulty starting the engine or stalling
- Check engine light is on or flashing
To fix spark plug and coil failure, you need to inspect the spark plugs and coils for any signs of damage, such as cracks, burns, or erosion. You also need to measure the resistance and voltage of the coils and compare them to the specifications. If the spark plugs or coils are faulty, you need to replace them with new ones that match the engine’s requirements. You may also need to check and replace other components of the ignition system, such as the wires, connectors, or distributor cap and rotor, if applicable.
2: Plastic intake failure
The intake manifold is a part of the engine that distributes the air-fuel mixture to the cylinders. Some intake manifolds are made of plastic, which can offer advantages such as lower weight and cost, but also disadvantages such as lower durability and heat resistance. Plastic intake failure can occur due to various reasons, such as:
- Cracks or leaks caused by thermal expansion and contraction, vibration, or impact
- Warping or melting caused by excessive heat from the engine or the exhaust gases
- Clogging or contamination caused by oil, coolant, or carbon deposits
Some common symptoms of plastic intake failure are:
- Engine performance issues, such as loss of power, rough idle, misfires, or hesitation
- Reduced fuel economy and increased emissions
- Coolant or oil leaks or consumption
- Check engine light is on or flashing
To fix plastic intake failure, you need to inspect the intake manifold for any signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, warping, or melting. You also need to check the intake manifold gasket, which seals the manifold to the cylinder head, for any signs of wear or leakage. If the intake manifold or gasket is faulty, you need to replace them with new ones that match the engine specifications. You may also need to clean or replace other components of the intake system, such as the throttle body, sensors, or injectors if they are affected by the intake failure.
3: Fuel pump driver module failure
The fuel pump driver module is a device that controls the operation of the fuel pump, which delivers fuel from the tank to the engine. The fuel pump driver module receives signals from the engine control module and provides the necessary power, voltage, and signals to the fuel pump. Fuel pump driver module failure can occur due to various reasons, such as:
- Corrosion or damage caused by moisture, salt, or road debris
- Overheating or short circuits caused by electrical issues or faulty wiring
- Wear and tear caused by age or usage
Some common symptoms of fuel pump driver module failure are:
- Engine performance issues, such as loss of power, rough idle, misfires, or hesitation
- Difficulty starting the engine or stalling
- Engine surging or jerking
- Check engine light is on or flashing
To fix fuel pump driver module failure, you need to inspect the fuel pump driver module for any signs of damage, such as corrosion, cracks, or burns. You also need to check the wiring and connectors for any signs of wear or damage. If the fuel pump driver module or the wiring is faulty, you need to replace them with new ones that match the vehicle specifications. You may also need to check and replace the fuel pump or the fuel pressure regulator if they are affected by the module failure.
4: Timing chain tensioner failure
The timing chain tensioner is a device that maintains the proper tension of the timing chain, which synchronizes the rotation of the camshaft and the crankshaft. The timing chain tensioner can be hydraulic or mechanical, depending on the engine design. Timing chain tensioner failure can occur due to various reasons, such as:
- Lack of lubrication or contamination of the lubricant
- Low oil pressure or oil level
- Wrong oil viscosity or quality
- Misalignment or vibration of the engine components
Some common symptoms of timing chain tensioner failure are:
- Engine performance issues, such as loss of power, rough idle, misfires, or hesitation
- Engine noise, such as rattling, knocking, or squealing
- Engine overheating or oil leaks
- Check engine light is on or flashing
To fix timing chain tensioner failure, you need to inspect the timing chain tensioner for any signs of damage, such as wear, cracks, or leaks. You also need to check the timing chain and the sprockets for any signs of wear or damage. If the timing chain tensioner, the chain, or the sprockets are faulty, you need to replace them with new ones that match the engine specifications. You may also need to check and adjust the valve timing if it is affected by the tensioner failure.
5: Oil leaks from the pan
The oil pan is a part of the engine that holds the engine oil and has a drain plug for oil changes. The oil pan is sealed to the engine block by an oil pan gasket. Oil leaks from pans can occur due to various reasons, such as:
- Loose or damaged drain plug or drain plug seal
- Cracked or rusty oil pan
- Hardened or worn oil pan gasket
- Damaged or loose oil pan bolts
Some common symptoms of oil leaks from the pan are:
- Low oil level or pressure
- Oil puddles or stains under the vehicle
- Engine noise, such as knocking or ticking
- Engine overheating or oil-burning smell
To fix oil leaks from the pan, you need to inspect the oil pan, the drain plug, and the gasket for any signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or corrosion. You also need to check the oil pan bolts for any signs of looseness or damage. If the oil pan, the drain plug, the gasket, or the bolts are faulty, you need to replace them with new ones that match the engine specifications. You may also need to check and replace the oil filter if it is affected by the oil leak.
Important Post: Flashing Check Engine Light Ford F150: What Does It Mean, Causes & Solutions
6: Underperforming oil pump
The oil pump is a device that circulates the engine oil to lubricate and cool the moving parts of the engine. The oil pump also maintains the oil pressure and prevents the engine from seizing. Underperforming oil pumps can occur due to various reasons, such as:
- Wear or damage of the oil pump components, such as the gears, rotors, or relief valve
- Clogging or restriction of the oil passages or the oil filter
- Low oil level or quality
- Wrong oil viscosity or type
Some common symptoms of an underperforming oil pump are:
- Low oil pressure or oil pressure warning light on
- Engine noise, such as knocking, ticking, or rattling
- Engine overheating or oil-burning smell
- Reduced engine performance or power
To fix an underperforming oil pump, you need to inspect the oil pump for any signs of damage, such as wear, cracks, or leaks. You also need to check the oil level, quality, and viscosity and change the oil and filter if needed. If the oil pump is faulty, you need to replace it with a new one that matches the engine specifications. You may also need to check and replace the oil pressure sensor, switch, or gauge if they are affected by the oil pump failure.
7: Broken exhaust manifold bolts
The exhaust manifold is a part of the engine that collects the exhaust gases from the cylinders and directs them to the exhaust pipe. The exhaust manifold is attached to the cylinder head by bolts or studs and sealed by a gasket. Broken exhaust manifold bolts can occur due to various reasons, such as:
- Corrosion or rust caused by moisture, salt, or road debris
- Overheating or expansion caused by excessive heat from the engine or the exhaust gases
- Over-tightening or under-tightening of the bolts or studs
- Vibration or misalignment of the engine components
Some common symptoms of broken exhaust manifold bolts are:
- Exhaust leak or noise, such as ticking, hissing, or popping
- Reduced engine performance, power, or fuel economy
- Increased emissions or engine smell
- Check engine light is on or flashing
To fix broken exhaust manifold bolts, you need to inspect the exhaust manifold for any signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or warping. You also need to check the exhaust manifold gasket for any signs of wear or leakage. If the exhaust manifold or gasket is faulty, you need to replace them with new ones that match the engine specifications. To remove the broken bolts or studs, you can use various methods, such as:
- Drilling into the center of the bolt using a drill bit that is a similar size to the bolt, then using a wrench to remove it
- Threading the bolt with a dye and hot welding or cold welding (J-B Weld) a nut to the bolt
- Using an air hammer or hammer/chisel to remove the bolt head if it cannot be turned with vice grips
- Using a special tool or kit designed for removing broken bolts or studs
After removing the broken bolts or studs, you need to clean the threads and install new ones that match the engine requirements. You may also need to check and replace other components of the exhaust system, such as the catalytic converter, the O2 sensor, or the muffler if they are affected by the exhaust leak.
8: Plastic intake failure
The intake manifold is a part of the engine that distributes the air-fuel mixture to the cylinders. Some intake manifolds are made of plastic, which can offer advantages such as lower weight and cost, but also disadvantages such as lower durability and heat resistance. Plastic intake failure can occur due to various reasons, such as:
- Cracks or leaks caused by thermal expansion and contraction, vibration, or impact
- Warping or melting caused by excessive heat from the engine or the exhaust gases
- Clogging or contamination caused by oil, coolant, or carbon deposits
Some common symptoms of plastic intake failure are:
- Engine performance issues, such as loss of power, rough idle, misfires, or hesitation
- Reduced fuel economy and increased emissions
- Coolant or oil leaks or consumption
- Check engine light is on or flashing
To fix plastic intake failure, you need to inspect the intake manifold for any signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, warping, or melting. You also need to check the intake manifold gasket, which seals the manifold to the cylinder head, for any signs of wear or leakage. If the intake manifold or gasket is faulty, you need to replace them with new ones that match the engine specifications. You may also need to clean or replace other components of the intake system, such as the throttle body, sensors, or injectors if they are affected by the intake failure.
Is The 3 Valve 5.4 Triton A Good Engine?

The 3-valve 5.4 Triton is a V8 engine that was produced by Ford from 2004 to 2014. It has some advantages over the previous 2 valve version, such as improved power, torque, and fuel efficiency, thanks to the variable camshaft timing system and the redesigned cylinder heads.
However, it also has some common problems, such as spark plug issues, cam phaser failures, and timing chain tensioner failures, which can be costly and difficult to repair. Therefore, the 3-valve 5.4 Triton engine is not considered a very reliable or durable engine by many experts and owners.
What Year Did Ford 5.4 Go To 3 Valve?
Ford introduced the 3-valve version of the 5.4 Triton engine in 2004 for some of its vehicle models, such as the Ford F-150, the Ford Expedition, and the Ford GT.
What Is The Most Common Problem With The 5.4 Triton?
The most common problem with the 5.4 Triton engine is the spark plug issue. This issue affects all versions of the 5.4 Triton engine, but especially the 2-valve model produced from 1997 to 2003.
The spark plugs can either get stuck in the cylinder head, break off, or blow out, causing damage to the engine and affecting its performance. The spark plug issue is caused by a combination of poor design, excessive heat, and internal pressure.
The spark plugs are too short and have only four threads to hold them in place, compared to 10-12 threads in most other engines. The spark plug-hole design is also flawed, as it allows dirt, water, and salt to corrode the aluminum threads and the coil boot.
The spark plug issue can be prevented or fixed by using the correct spark plugs and tools, replacing the coil boot and the ignition coil, and repairing or replacing the cylinder head if needed.
How Do I Know If My 5.4 Is 2 Or 3 Valve?
Here is how you can tell if your 5.4 engine is 2 valves or 3 valves:
- Check the air filter housing. If it has 3V written on it, then you have a 3-valve engine. If it does not, then you have a 2 valve engine.
- Check the VIN. The 8th digit of the VIN is the engine code. If it is L, then you have a 2-valve engine. If it is 5, then you have a 3-valve engine.
- Check the coils. If the rubber part that slips over the spark plug has a bend in it, then you have a 2 valve engine. If it is straight, then you have a 3-valve engine.
What Are The Advantages & Disadvantages Of A 3 Valve Engine?
Some of the advantages of a 3-valve engine are:
- Better fuel efficiency: A 3-valve engine uses less fuel while delivering the same power, making it more fuel-efficient.
- Improved engine performance: The design of a 3-valve engine allows for smoother operations, leading to improved overall engine performance.
- Lower emissions: Due to the optimized combustion process, a 3-valve engine produces fewer pollutants, contributing to lower emissions.
- Enhanced engine cooling: The unique arrangement of the valves in a 3-valve engine allows for better heat dissipation, resulting in enhanced engine cooling.
- More power output: The efficient design of a 3-valve engine allows it to produce more power output compared to other engine types.
Some of the disadvantages of a 3-valve engine are:
- Less fuel-efficient: A 3-valve engine uses more fuel than other types, making it less fuel-efficient. This means it is not the best choice for long drives or frequent use.
- More complex design: A 3-valve engine has a more intricate design, which can make it harder to understand and repair. This complexity can be a problem for mechanics and car owners.
- Higher manufacturing cost: Because of its complex design, a 3-valve engine is more expensive to manufacture. This higher cost often gets passed on to the consumer, making the vehicles more expensive.
- Increased maintenance needs: A 3-valve engine requires more frequent and intensive maintenance. This can be both time-consuming and costly for the owner.
- Not ideal for high speeds: Despite its power, a 3-valve engine is not ideal for high speeds. It may not perform as well in fast-driving scenarios, limiting its versatility.
When Did Ford Stop Using The 5.4 3 Valve?
Ford stopped using the 5.4 3-valve engine in some of its vehicle models between 2006 and 2014. Some of the vehicle models that used the 5.4 3-valve engine were:
- Ford F-150 (2003-2007)
- Ford Falcon (2004-2007)
- Ford GT (2004-2006)
- Ford Mustang SVT Cobra R (2000)
What Is The Difference Between A 2-valve And A 3-Valve Engine?
The difference between a 2-valve and a 3-valve engine is mainly in the number and arrangement of the valves that control the flow of air and fuel into the combustion chamber.
Valves are the openings on the cylinder head that allow the air-fuel mixture to enter and the exhaust gases to exit. A 2-valve engine has one intake valve and one exhaust valve per cylinder, while a 3-valve engine has two intake valves and one exhaust valve per cylinder.
The main advantage of a 3-valve engine over a 2-valve engine is that it can allow more air to enter the combustion chamber, which improves the engine’s breathing and performance.
A 3-valve engine can also have better fuel efficiency and lower emissions than a 2-valve engine, as it can optimize the combustion process.
However, a 3-valve engine is more complex and costly to design and produce than a 2-valve engine, and it may require more maintenance and tuning.
A 2-valve engine, on the other hand, is simpler and cheaper to make and operate, and it may have more low-end torque and reliability than a 3-valve engine.
How many spark plugs does a 5.4 Triton have?
The Ford 5.4L Triton is a V8 engine, which means it has 8 cylinders. Each cylinder requires its own spark plug, so you will need a total of 8 spark plugs for a full replacement.
Related Article: Ford Triton V10 Engine: A Detailed Explanation Of This Gem!
How do I know what Ford engine I have?
To identify your Ford engine, you need to look for the identification tag or the casting number on the engine block.
The identification tag is a metal plate that has information such as the engine size, model year, and manufacturing plant.
The casting number is a series of digits and letters that indicate the date and location of production, as well as the engine type and displacement.
Depending on the engine model, you may find the tag or the casting number in different locations, such as under the coil, the dipstick, the heat indicator bulb, or the carburetor stud.
You can also count the number of valve cover bolts to narrow down the engine family. For example, a 6-bolt valve cover indicates a 221/260/289/302/351W engine, while an 8-bolt valve cover indicates a 351C/351M/400 engine.
How much oil does a 5.4 Ford engine take?
The Ford 5.4 engine has an oil capacity of 6 quarts, which is around 5.7 liters. The recommended type of oil for this engine is fully synthetic 5W-20 or 5W-3012. You should change the oil regularly to keep your engine in good condition.
How long will a Triton engine last?
A Triton engine is a type of V8 engine that Ford has used in many of its vehicles since 1997.
The life expectancy of a Triton engine depends on several factors, such as maintenance, driving habits, and model year.
On average, a Ford 5.4 engine will last between 150,000 and 300,000 miles.
However, with proper care, some Ford 5.4 engines can last up to 450,000 miles or more.
What Is Ford 5.4 3 Valve Engine Horsepower?
This engine has a horsepower range of 295-327 hp at 5,000 rpm, depending on the model and year of the vehicle. The engine also has a torque range of 330-369 lb-ft at 3,500 rpm.
The Ford 5.4 3 Valve Engine features variable camshaft timing, which improves power, torque, and fuel efficiency over the previous 2-valve version. The engine has a cast iron block, aluminum heads, and three valves per cylinder.
Some of the vehicles that use the Ford 5.4 3 Valve Engine are the Ford F-150, Ford Expedition, Ford E-Series, and Lincoln Navigator.
Conclusion
We have covered the common Ford 5.4 3-valve engine problems, their causes, symptoms, and solutions.
We have also discussed the reliability and performance of this engine and whether it is worth buying or not.
The Ford 5.4 3-valve engine is a powerful and advanced engine that belongs to the Modular family of Ford engines.
It has some innovative features such as variable camshaft timing and three valves per cylinder.
However, it also has some drawbacks, such as spark plug failure, timing chain rattles, oil leaks, and more.
These problems can be costly and time-consuming to fix, and they can affect the overall quality and durability of the engine.
Therefore, if you are planning to buy a Ford vehicle with a 5.4 3-valve engine, you should be aware of these potential issues and do a thorough inspection before making a purchase.
You should also maintain the engine properly and follow the recommended service intervals.
By doing so, you can extend the lifespan of the engine and enjoy its benefits.
We hope this article has been informative and helpful for you.
Thank you for reading and have a great day!